A cpu can have anywhere from tens of millions to billions of transistors. The number of transistors in a cpu largely depends on the manufacturing process used, with smaller transistors resulting in higher transistor counts.
Central processing units (cpus) are the brain of a computer, responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations. A cpu is made up of small electronic devices called transistors, which turn on and off to perform tasks. Over time, the number of transistors in cpus has increased exponentially with the advances in technology, allowing for more powerful and efficient computing.
The number of transistors in a cpu is largely dependent on the manufacturing process used, with smaller transistors allowing for higher transistor counts. Today’s cpus can have anywhere from tens of millions to billions of transistors, making them incredibly powerful and efficient computing machines.
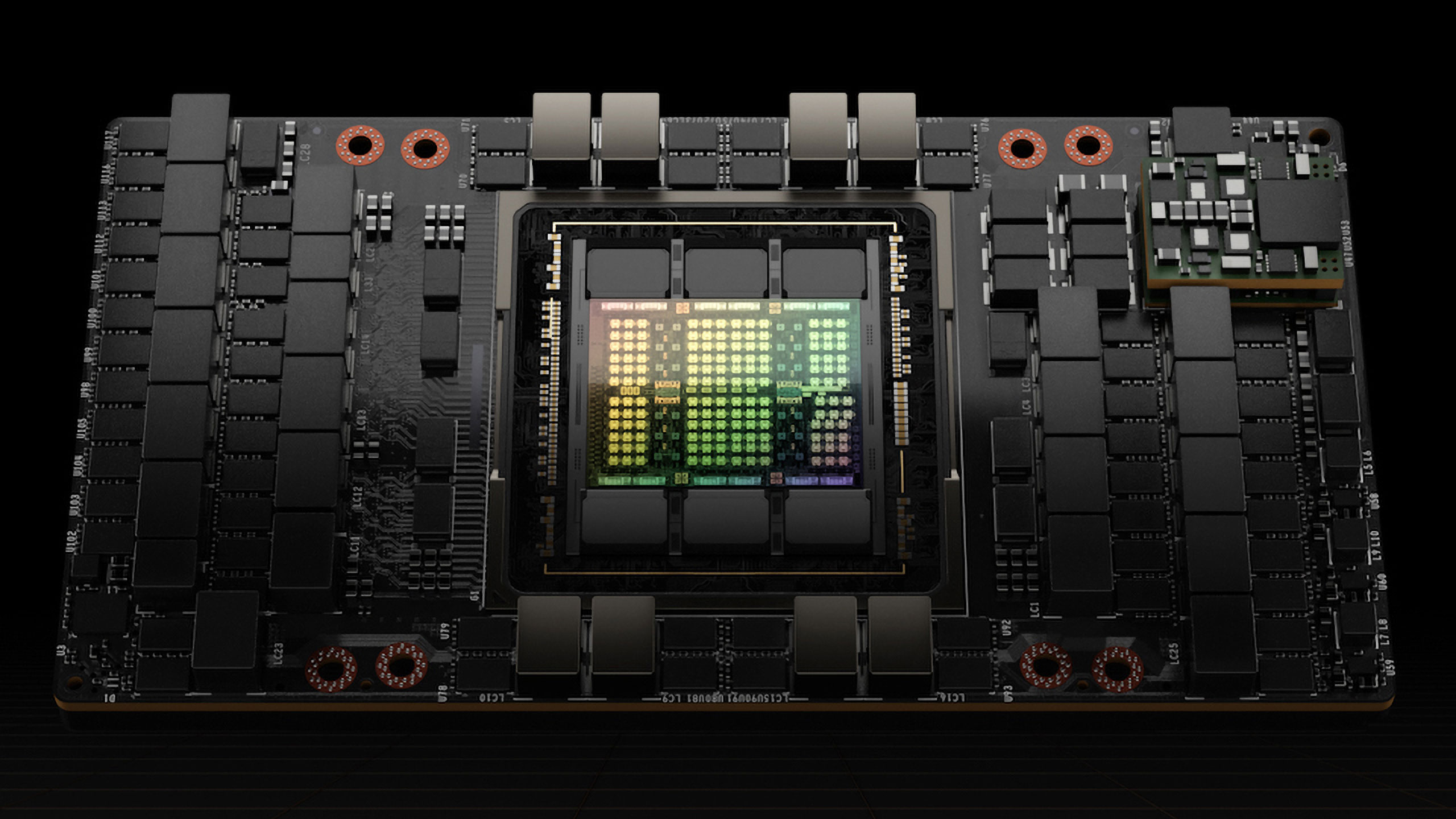

Credit: www.tomshardware.com
What Are Transistors?
Definition Of Transistors
Before we dive into talking about how many transistors are in a cpu, it’s important to have a fundamental understanding of what transistors are. Here’s what you need to know:
- Transistors are tiny, semiconductor devices that act as switches or amplifiers for electronic signals.
- They are an essential component of modern electronics, including cpus, because of their ability to control and manipulate electrical currents.
- Invented in 1947, transistors replaced bulky vacuum tubes and led to the development of smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic devices.
How Transistors Function In A Cpu
Now that we know what transistors are, let’s take a look at how they work inside a cpu:
- A cpu integrates millions, or even billions, of transistors to perform arithmetic, logic, and control operations.
- When an electrical current passes through the transistor, it either allows or blocks the flow of that current, depending on its configuration.
- By controlling the flow of electrical currents, the cpu can execute different instructions and calculations, resulting in the organized and efficient operation of your computer.
Brief History Of The Development Of Transistors
It’s fascinating to reflect on how far technology has come since the invention of transistors in 1947, and how they have transformed the world as we know it today. Here are some key milestones to keep in mind:
- The first transistor was invented in 1947 at bell labs by john bardeen, walter brattain, and william shockley.
- In 1956, the first transistorized computer was developed, which was faster, smaller, and more reliable than previous computer models.
- The development of microprocessors in the early 1970s marked the beginning of a new era in computing, as they integrated an entire cpu on a single chip, providing unprecedented processing power.
- Today, processors such as intel and amd can pack over 10 billion transistors on a single chip, allowing for the development of complex applications and high-performance computing.
In sum, transistors are a vital component of modern computing, allowing for the impressive processing power of today’s computers and other electronics. The continual evolution of transistors is a testament to the incredible advancements in technology we continue to witness.
How Many Transistors Are In A Cpu?
Explanation Of How Transistors Size And Count Has Evolved Over Time
From the first computer, eniac, which was created in the 1940s, to the modern computer, the evolution of cpus has been remarkable. The transistor, which is a semiconductor device that amplifies or switches electronic signals, plays a significant role in the cpu’s performance.
In the early days, computers had only a few thousand transistors, while today’s cpus have several billion. The size of the transistors has decreased significantly over time, which has resulted in an increase in their count. In the beginning, the size of the transistor was around 10 microns, while today’s cpus have transistors that are less than 10nm.
Key Factors That Determine Transistor Count In A Cpu
The transistor count in a cpu is determined by a variety of factors, including:
- The operating frequency of the cpu
- The number of cores in the cpu
- The size of the wafer on which the cpu is built
- The manufacturing process used to create the cpu
Manufacturers try to increase the transistor count in cpus while keeping the power consumption low. This is because as the transistor count increases, so does the power consumption, which leads to more heat generation. To reduce power consumption, manufacturers use the latest manufacturing processes and technologies, which allow them to create more efficient and smaller transistors.
Comparison Of Transistor Count In Cpus Over Time
The transistor count in cpus has increased significantly over time, as manufacturers have been able to create smaller and more efficient transistors. Here’s a comparison of transistor counts in cpus over time.
- The first cpu, intel 4004, released in 1971 had only 2300 transistors.
- In 1993, intel released the pentium processor, which had 3.1 million transistors.
- In 2000, intel announced the pentium 4 processor, which had 42 million transistors.
- In 2016, intel released the xeon phi processor, which had around 8 billion transistors.
- In 2021, amd launched the ryzen 9 5950x processor, which had around 16 billion transistors.
This shows that the transistor count in cpus has increased exponentially over the years, leading to better performance and efficiency.
Importance Of Transistor Count In Cpus
How Transistor Count Affects Cpu Performance
Central processing units (cpus) are electronic devices that facilitate computer operations by processing data. A cpu comprises electronic components that handle calculations and instructions. These electronic components are called transistors. The higher the number of transistors present in the cpu, the better its performance.
- Transistors are the basic building blocks of cpus.
- The number of transistors in cpus influences their performance.
- More transistors in a cpu lead to better performance.
Explanation Of Moore’S Law And Its Impact On Transistor Count
In 1965, gordon moore, co-founder of intel, predicted that the number of transistors on an integrated circuit would double every two years. This prediction, known as moore’s law, has proven accurate for over five decades.
- Moore’s law states that transistor count on an integrated circuit doubles every two years.
- Moore’s law has held true for over five decades.
- This doubling of transistor count has been the key driver of cpu performance.
Examples Of How Added Transistors Have Improved Cpu Capabilities
As predicted by moore’s law, cpu manufacturers have improved the performance of cpus over time by adding more transistors.
- The 4004 microprocessor, released by intel in 1971, had 2,300 transistors.
- In comparison, the current generation of cpus, such as the apple m1, have over 16 billion transistors.
- The addition of transistors has led to improvements in cpu capabilities such as faster processing speeds, improved ai capabilities, and better energy efficiency.
Transistors are the building blocks of cpus and impact their performance. Moore’s law has been the key driver of cpu performance improvements over the years. The addition of more transistors has led to significant improvements in cpu capabilities, including faster processing speeds and better energy efficiency.
Future Of Transistor Count In Cpus
The future of transistor count in cpus is an intriguing topic that has gotten everybody talking. On one hand, we have advanced technology that has enabled us to fit more transistors onto a tiny piece of silicon. On the other hand, there is a limit to how much we can increase the number of transistors on a cpu.
Here are some key points to keep in mind when we try to predict the future of the transistor count in cpus.
- The physical limits of transistors: As we increase the number of transistors, we reach a point where they are so small that the electrons can tunnel through the barriers, causing voltage leaks, and making the cpu less efficient. Working around this will require significant advancements in material science and nanotechnology.
- The cost vs. Benefit analysis: We need to weigh the cost of manufacturing cpus with an increasing number of transistors against the performance gains. If the cost outweighs the benefits, the trend may slow down.
- The rise of quantum computing: Quantum computing is still in its infancy, but it has the potential to revolutionize the industry. It is too early to predict if transistors will play a significant role, or if there will be alternative ways to achieve better performance.
Discussion Of Potential Limits To Transistor Count In Cpus
The limits of transistor counts in cpus are both technological and economical. Here are some of the potential limitations that we may encounter.
- The size of transistors: There are physical limits to how small transistors can be etched on silicon. Making them too small will pose technological challenges to performance.
- Quantum tunneling: The phenomenon of quantum tunneling can cause electrons to jump across barriers, which causes energy dependence and reduces transistor efficiency. Solving this problem requires significant breakthroughs in quantum mechanics.
- Economical feasibility: Increasing the number of transistors on a cpu also increases their production cost, and it becomes less economically feasible at some point.
Exploration Of Alternative Approaches To Improving Cpu Performance
Cpu manufacturers are continuously exploring alternative ways of improving performance beyond increasing transistor counts. Here are some of the promising options they are looking into:
- Parallel processing: Cpus with multiple cores can perform more tasks simultaneously, leading to increased performance without an increase in the transistor count.
- Specialized computing: Specialized chips like graphics processing units (gpus) and field programmable gate arrays (fpgas) can offload specific tasks from cpus, freeing them to do other things.
- Neuromorphic computing: Neuromorphic computing is a new approach that mimics biological neurons to process information better than traditional cpus. This is still experimental, and we don’t know how it will evolve.
Consideration Of The Role Of Transistor Count In Future Technological Advances
The role of transistors in future technological advances is fundamental. Here is what we can expect.
- Continued advancements in artificial intelligence (ai): Ai algorithms require colossal amounts of computing power, and this will continue to drive innovations in cpu technology.
- Internet of things (iot): The increasing number of connected devices requires smaller, efficient, and cheaper cpus.
- Quantum computing: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize the industry, but it is still in its early stages of development. However, if it materializes, it could bring significant technological advancements.
As we have seen, the future of transistor counts in cpus is a nuanced subject. While we can expect improvements in performance, there are limits to how many transistors we can add to a cpu. Nevertheless, there are alternative approaches to achieving better performance, and as technology advances, cpus will play a critical role in future technological advances.
Frequently Asked Questions On How Many Transistors In A Cpu
How Many Transistors Are In A Cpu?
A modern cpu has billions of transistors that are used to carry out millions of calculations in mere seconds.
What Do The Transistors Do In A Cpu?
Transistors in a cpu regulate the flow of electrical current, functioning as switches or amplifiers to control digital information.
How Does The Number Of Transistors Impact Cpu Performance?
The number of transistors in a cpu impacts its performance as it determines the amount of information it can process at any particular time.
Conclusion
The cpu is an integral part of modern computers, and the number of transistors in it plays a crucial role in its performance. The ever-evolving technology has made it possible to increase the number of transistors in cpus over the years, resulting in better and faster performance.
As we have seen, the number of transistors in a cpu has increased from a few thousand in the 1970s to billions in current cpus. With the advancement of technology, the number of transistors is expected to continue to increase, allowing for even better performance and efficiency in our computing devices.
It is important to note that while the number of transistors is important, other factors such as the architecture of the cpu also contribute significantly to its performance. That being said, it is safe to say that the number of transistors in a cpu is a crucial aspect that should be considered when purchasing a new computer or upgrading an existing one.